[wpsm_titlebox title=”Contents” style=”1″][contents h2 h3][/wpsm_titlebox]
Free WordPress Tutorials and Courses for Novices
Learn the fundamentals of WordPress by following along with one of these two amazing and totally free courses geared at novices. You may go from knowing nothing at all to being able to establish a WordPress website and even begin tweaking and coding your own themes with the help of these instructions. For further information, subscribe to the Tuts+ channel on YouTube.
What are Some Reasons You Might Want to Learn WordPress?
WordPress is one of the most widely used open-source content management system (CMS) frameworks. You may use it to develop websites of varying complexity, from simple blogs to fully functional online stores. It is quite simple to use, and it can be installed on your server in a matter of minutes. According to the statistics, WordPress is used to power nearly 38% to 40% of all websites, and each day, new websites are added to its roster of clients.
WordPress is a content management system that enables website administrators to develop websites relatively simply and fast. As a result of its widespread usage, there are literally thousands upon thousands of pre-made themes and plugins that are at your disposal. In addition to that, the administrative control panel of your website may have other tools, such as page builders, that enable you to fully personalize the appearance of your website.
On the other hand, WordPress is totally open to the developers’ personalization in any way they see fit. If you educate yourself on how to develop custom plugins and themes for use with WordPress, there is very little that you won’t be able to do.
Today, we’ll investigate WordPress from two different vantage points: that of a site administrator and that of a developer.
Figure out how to use WordPress.
In this part of the tutorial, we’ll look at the dashboard that comes with WordPress.
Before we continue, I will assume that you have a functioning installation of WordPress and that you have access to the administrative dashboard. In the event that you have not yet installed WordPress or are unsure of how to do so, we have written an article that provides a step-by-step guide to the installation procedure. After you have completed the installation, we will be able to proceed to the next step.
Dashboard Overview
The WordPress administrative interface presents the dashboard in the form depicted in the following snapshot after you have successfully logged in.
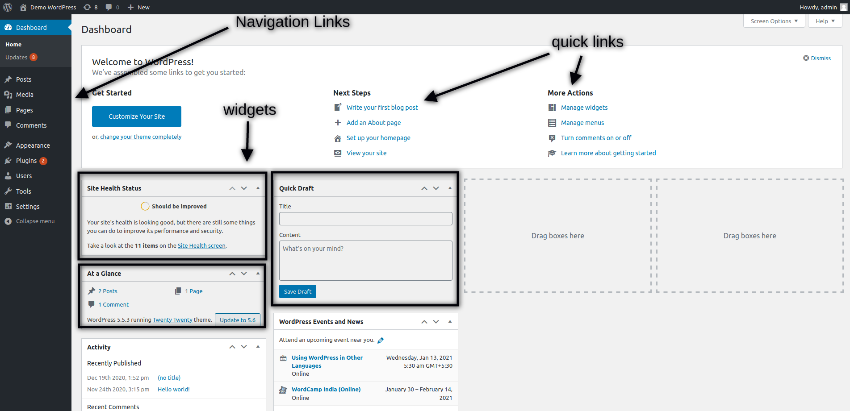
On the left hand side, it displays the main navigation links that you could use to navigate to the different sections of the website. On the right hand side, it displays a few quick links and a few widgets like Activity, At a Glance, Site Health Status and more. You could use the drag-and-drop feature to reorder widgets, and you could also display more widgets on the dashboard as per the requirements.
Now, we’ll briefly discuss the important sections on the dashboard.
Posts
It’s difficult to imagine a WordPress site without posts. In fact, posts are the heart of any WordPress website. Mainly they allow you to manage categories and posts on your website. You can add new posts, as well as edit and delete existing posts in this section. This is the section you will deal with most of the time.
Media
When you create content on your website, you may need to embed different types of media files along with the text content, it could be images, videos, pdf files and alike. The media section is a central place where you could manage all media files of your website. Once you upload files in this section, it would be available to you when you create posts or pages.
Pages
In this section, you can manage the static pages of your website. A page in WordPress is a different type of content which you want to use when you create a content which is purely static and doesn’t need publishing features.
Comments
The comments section allows you to manage post comments that are made by users. You could perform different operations like Approve, Unapprove, Mark as Spam and Move to trash.
Appearance
The appearance section allows you to configure and control theme-related aspects of your website. In fact, it provides a whole lot of options that you can use to change the look and feel of your website. Importantly, it allows you to install new themes and switch between different themes.
Plugins
The plugin section allows you to install and configure third-party plugins in your website. The WordPress marketplace provides thousands of the plugins, so you can find and install plugins for any feature.
Users
The users section allows you to manage users in your website. You could create different types of users like Subscriber, Contributor, Author, Editor and Admin.
Settings
In this section, you can configure the global settings of your website. It contains various settings like date format in posts, thumbnail image size, or number of posts to display.
How to Create Your First Post
In this section, we’ll see how to create posts in WordPress.
Head over to the back-end and go to the Posts > Add New section. It should open the following UI.
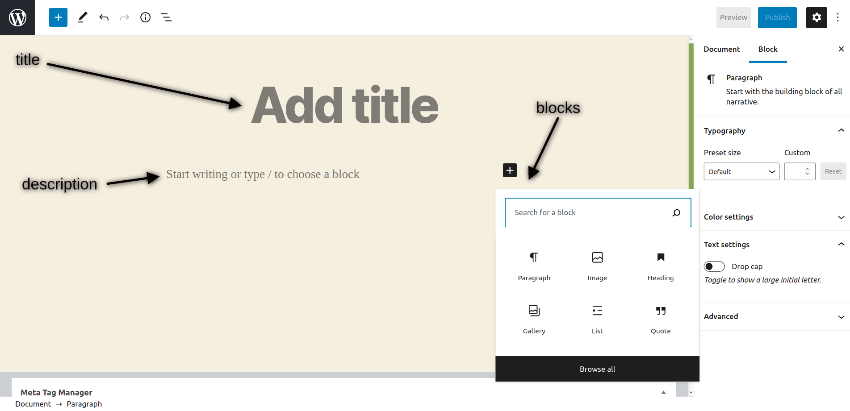
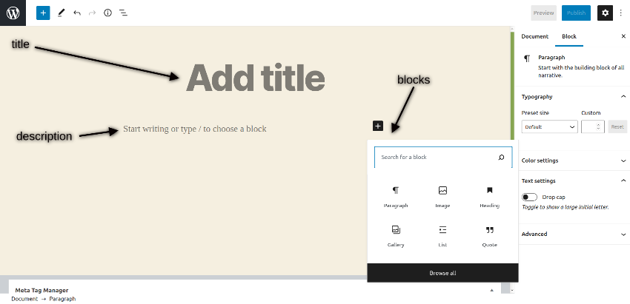
It provides a nice and intuitive UI which makes it easy for you to create and publish posts effortlessly. You can add title, description and configure different settings of the post. In the description section, you could insert different blocks like paragraph, quote, image, heading etc. to add different types of content. It allows you to format your posts according to the different types of blocks.
Apart from this, you could assign a post to the specific category, add featured image and do a couple of more settings under the Document tab on the right hand side.
Once you’ve entered the content, click on the Publish button on the top right to publish the post! Head over to the front-end, go to that post. In my case, it looks like this!
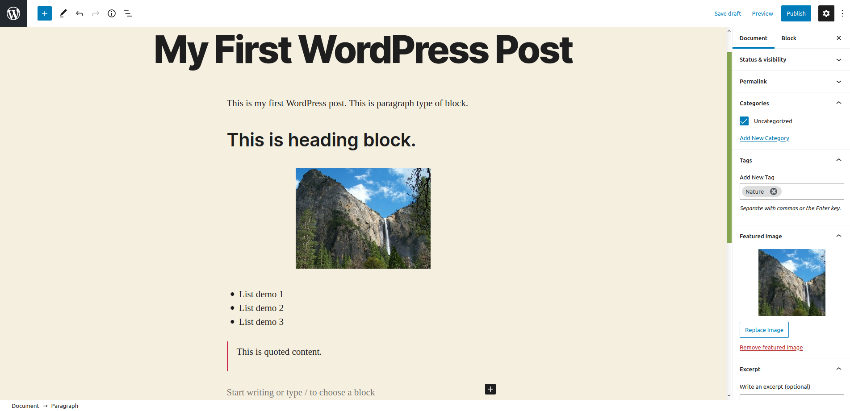
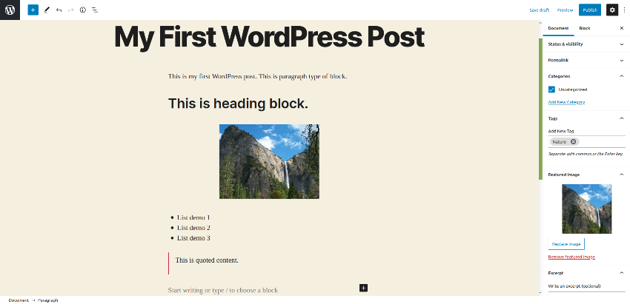
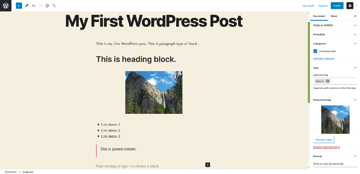
So that’s how you could create blog posts from the back-end. Similarly, you could add static pages as well under the Pages section.
How to Use the Media Manager
In this section, we’ll see how you could manage different types of media files in WordPress.
Head over to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Media > Add New. It will display the following screen.
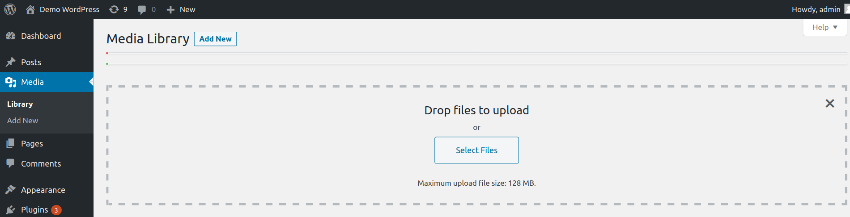
Click on the Select Files button, which allows you to choose files from your computer that you want to upload. Select the desired files, and they’ll be uploaded right away, as shown in the following screenshot.
Navigate to the Media > Library section, and it should display the list of files that is already available. If you want to view or modify any file details, click on the file which you’ve just uploaded to see the file details.
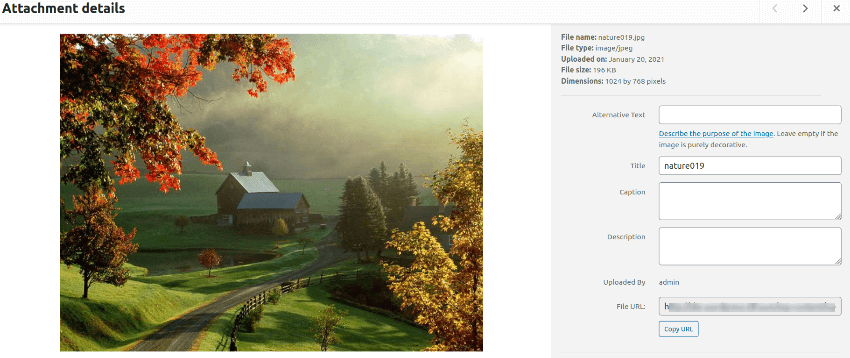
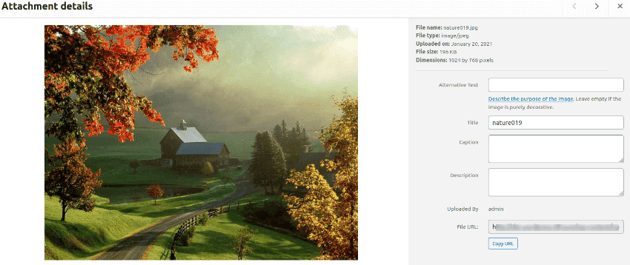
The above UI allows you to edit the image, add a few image details like caption, description etc.
In this way, you could manage files with the Media manager.
WordPress Themes
In this section, we’ll discuss WordPress themes. A WordPress theme is responsible for the look and feel of your website. By default, WordPress provides a couple of basic themes to start with, but you could always download and install third-party themes of your choice. Of course, you could build your custom theme as well if you want to customize the front-end as per your requirements.
How to Activate Themes
Go to the Appearance > Themes section, and it should list out the built-in themes as shown in the following screenshot.
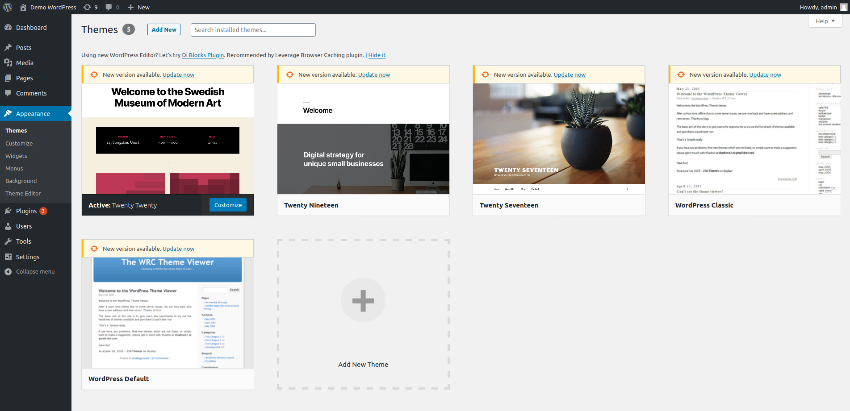
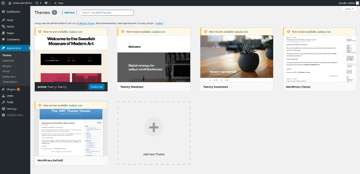
The default theme in WordPress is Twenty Twenty, and you could see it as an active theme. If you want to activate any other theme, you just need to click on the Activate button as shown in the following screenshot.
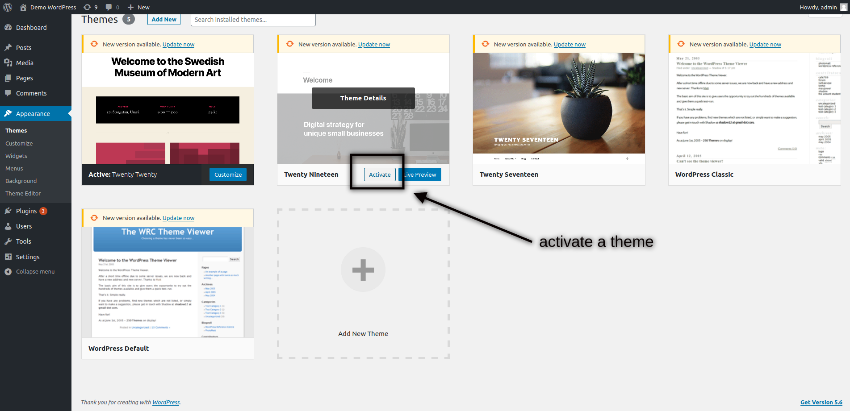
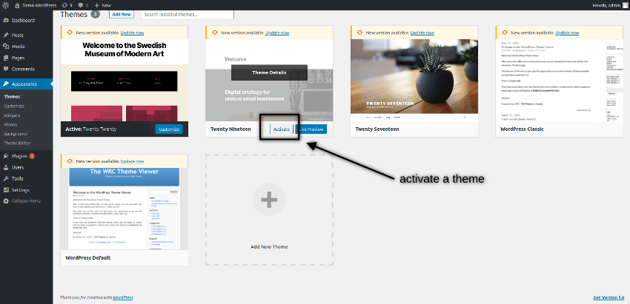
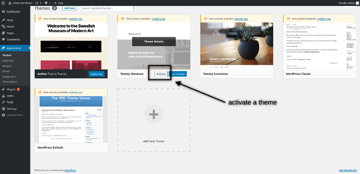
How to Customize the Default Theme Settings
For each theme, you could customize a few settings under the theme configuration section. Let’s quickly go through how to do it. Click on the Customize button for the active theme as shown in the following screenshot.
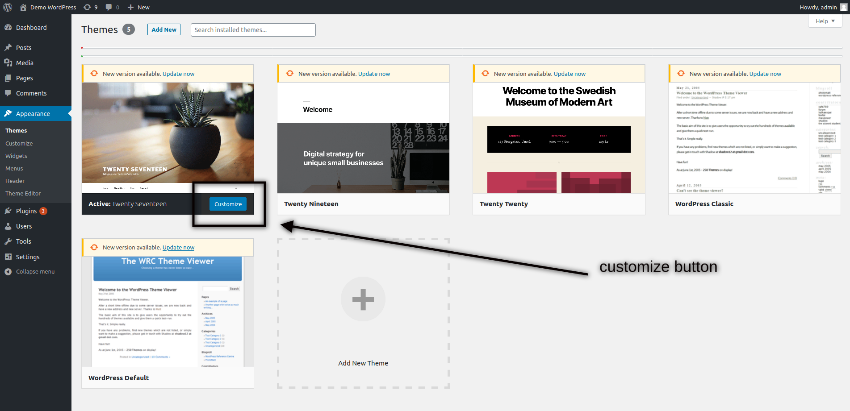
Once you click on the customize button, it takes you to the following page.
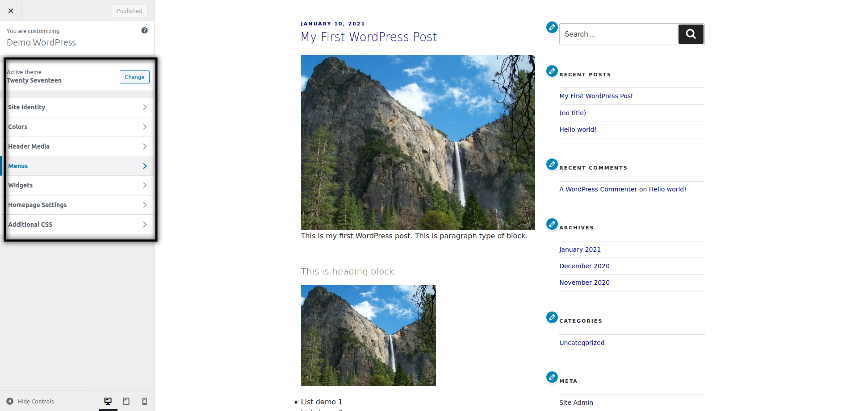
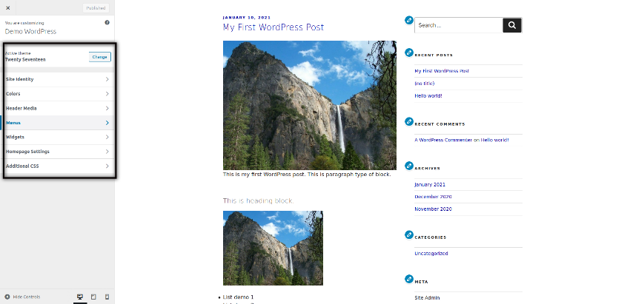
Here you can configure different settings like Site identity, Colors, Additional CSS, Menus and more. These settings are theme specific settings, so it’s up to the theme provider how many settings they provide in the configuration section. If you’re using an advanced theme, you would see a whole lot of configuration options in this section.
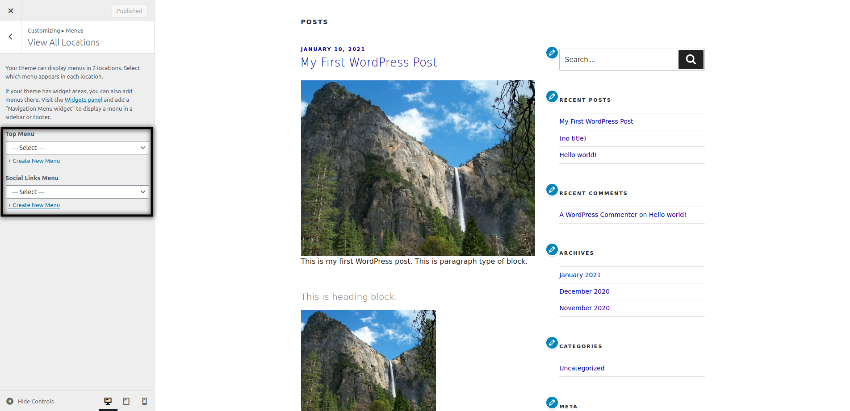
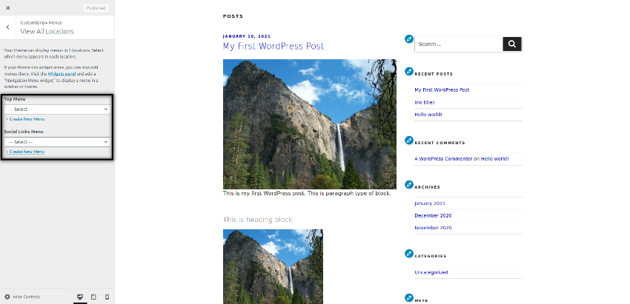
Specifically, Menus and Widgets settings are important ones. Menus settings allow you to display menus at different locations supported by the active theme. In the following screenshot, you could see that the active theme supports two locations: Top Menu and Social Links Menu.
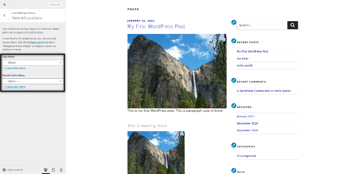
On the other hand, widgets are blocks that are displayed at different positions of your web page like left sidebar, right sidebar, footer-1, footer-2 etc. Widgets are really useful in a way that they add content and features to your website. For example, you could have different widgets like recent posts, most viewed posts, image galleries, recent comments and many more.
It’s up to template to provide different widget positions that you could use to display content. For example, the Twenty Seventeen theme provides three widget positions as shown in the following screenshot. You could also see the widgets preview on the right hand side.
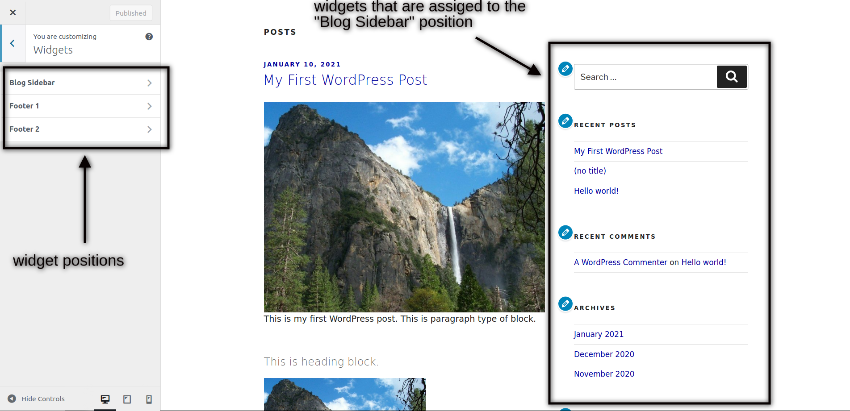
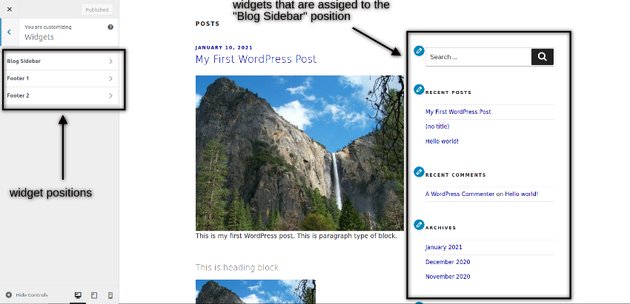
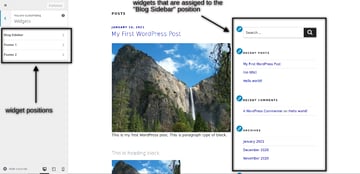
If you want to add a new widget, you just need to click on the widget position. Once you click on that, you could use the Add a Widget button to add widgets in that position. When you click on the Add a Widget button, it allows you to choose from the different types of widgets as shown in the following screenshot.
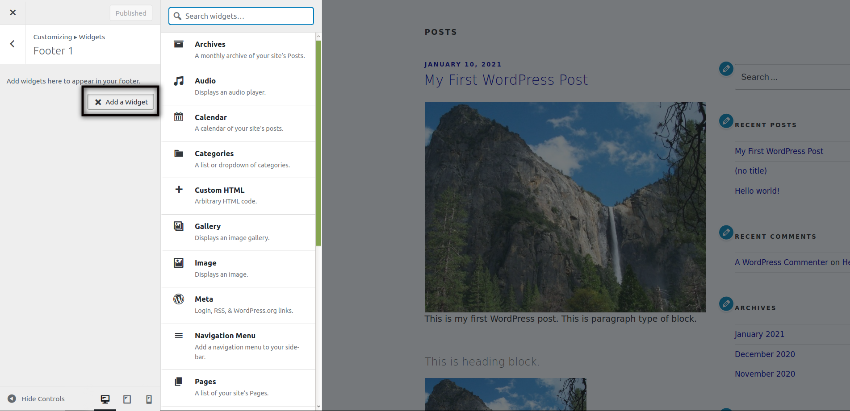
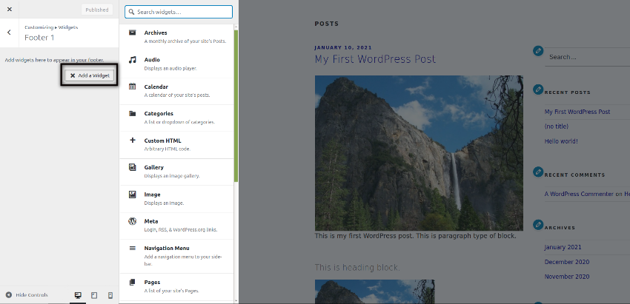
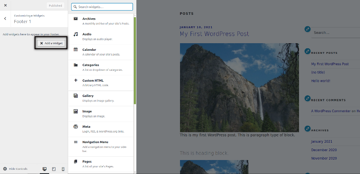
As you could see, you could choose from the different types of widgets like Archives, Audio, Custom HTML and many more. Feel free to play with it and observe the changes in the front-end.
How to Install Themes
Although, built-in WordPress themes are a great starting point and good to experiment with, if you want to build a professional website, you would like to use a third-party theme or build your own custom theme. In this section, we’ll discuss how you can install third-party themes.
When you purchase or download a theme, you would get a .zip theme file which is used for theme installation. Go to the Appearance > Themes section, and click on the Add New button. Next, click on the Upload Theme button which opens the following popup.
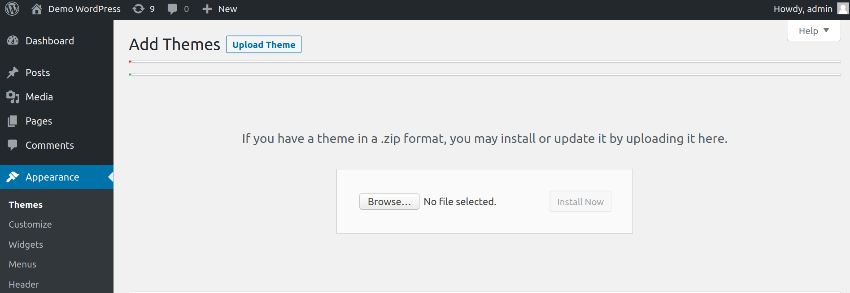
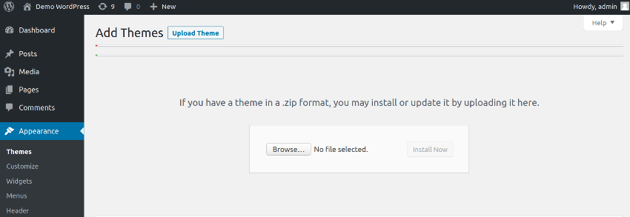
Installing the.zip file requires you to first upload it by clicking the Browse button, and then you must click the Install Now button. And with that, a WordPress theme has been effectively installed on your website!
In conclusion, that wraps up my condensed tour of WordPress themes.
WordPress Add-ons and Plugins
Because WordPress is a content management system (CMS) and a platform for blogging at its core, the basic features of WordPress focus on these two functions. WordPress plugins are what you should seek for if you wish to enhance the functionality of WordPress by adding new features.
A WordPress Plugin is a third-party package that can be installed on your site to improve the functionality of WordPress. Plugins may be found in the WordPress plugin directory. There are many of free plugins that can be downloaded from the WordPress marketplace, but if you want more sophisticated capabilities, you can also buy premium plugins.
You could, for instance, install an e-commerce plugin on your website, which would then function as an online shopping cart once it was activated. On the other hand, you may transform your website into an online gateway by using a number of different plugins in conjunction with one another. Therefore, all you need to do is conduct a search for the appropriate plugins that meet your criteria, download them, and then install them on your website.
The Step-by-Step Guide to Installing WordPress Plugins
The process of installing WordPress plugins is rather similar to that of installing themes, and we have previously covered it in a previous section.
To add a plugin developed by a third party, go to the Plugins > Add New menu option. Next, choose the plugin you want to add by clicking on the Upload Plugin button. This will bring up a window where you may select the plugin’s.zip file to add. In order to complete the installation, click the box labeled Install Now. You’ve just finished a successful installation of a WordPress plugin. Congratulations!
The Step-by-Step Guide to Mastering WordPress Development
In this part of the article, we will talk about WordPress from the perspective of a developer. I’ll point out a number of things you may start with if you’re interested in developing for WordPress and want to become a WordPress developer.
Technologies WordPress is Constructed Using
PHP, which is one of the most common server-side scripting languages used for web development, and MySQL, which is an open-source relational database management system, are the primary building blocks of WordPress. In addition to that, it requires the use of a web server application such as Apache, Nginx, or IIS.
Before you start working with WordPress, you should become familiar with PHP and MySQL if you haven’t already done so. On the other side, if you already know it and you’ve previously constructed websites based on it, starting to learn WordPress should be simple for you to do since WordPress is based on what you already know.
What Types of WordPress Development Skills Should You Acquire?
When it comes to developing custom features for WordPress, there are primarily two areas on which you should concentrate your efforts and become an expert.
custom plugin development
design and creation of bespoke themes
You will get familiar with the inner workings of WordPress, its APIs, and a great deal more as you walk through the process of learning how to design custom themes and plugins.
Development of Individualized Plugins
As was just said, WordPress plugins extend the capabilities of WordPress by layering additional functionality on top of its core capability. In point of fact, it is impossible to envisage a WordPress website that exists in the real world and operates without the need of any third-party plugins. If you are able to understand custom plugin creation, you will be able to add custom features on top of WordPress. Since WordPress websites need plugins in some form or another, this opens the door for you to add such features.
The construction of custom plugins is more closely related to programming, and it is essential to have a thorough grasp of the fundamentals of both PHP and MySQL before beginning. If you have previous knowledge with programming, getting started with this ought to be extremely simple for you.
Development of Individualized Themes
If developing plugins is more of a programming-focused endeavor, then developing custom themes is more of a designing-focused one. It is possible to entirely transform the appearance of your website by selecting one of the tens of thousands of third-party themes that are now accessible. These themes may be downloaded for free or for a charge and then activated.
Learning how to use software like Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator, which are programs that let you design websites, is necessary if you want to have a career as a professional theme developer. After that, you will need to turn the design into an HTML document. And lastly, you would get familiar with the structure of the WordPress theme, which would allow you to transform the HTML into the WordPress theme.
