[ad_1]
We’ll create this in two alternative ways so that you just get understanding of varied CSS properties. You should utilize this UI sample in several elements of your websites, for instance:
- To current staff members
- To indicate featured or newest posts/merchandise
- To record testimonials
As with every new CSS options, you may see inconsistencies relying on the browser you employ to test the demos. For instance, Chrome will present our customized scrollbar, whereas Firefox will nonetheless present the default scrollbar. Hold this in thoughts, and remember to test caniuse.com for the browser assist of varied front-end options.
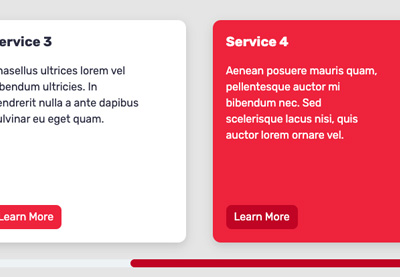
Our Scrolling Card UI
Examine the primary model of our completed part that makes use of flexbox for the grid format:
And this is the second model of our completed part that makes use of CSS Grid for the grid format:
Attempt scrolling each in order that half a card is seen on the edge—see how the scrolling conduct mechanically snaps the playing cards into place!
1. Decide the Structure
Let’s kick issues off by discussing the undertaking necessities.
We have to create an adaptive scrollable card format. The variety of playing cards that may seem in view will change relying on the viewport dimension.
Right here’s a useful desk the place we register how our format (grid) ought to behave on totally different screens:
| Display | Viewport Measurement | Grid Columns | Grid Hole |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-Small | < 500px | 1 | 10px |
| Small | ≥ 500px | 2 | 20px |
| Medium | ≥ 700px | 3 | 30px |
| Massive | ≥ 1100px | 4 | 40px |
To visualise issues, on additional small screens, the format will seem like this:

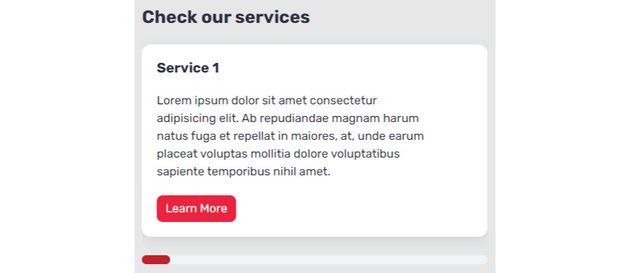
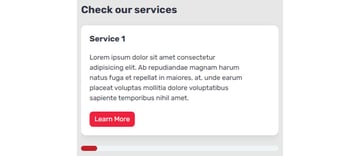
On small screens, it would seem like this:
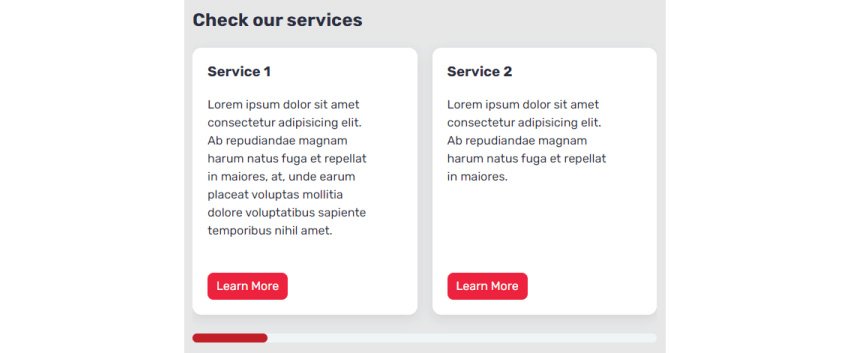
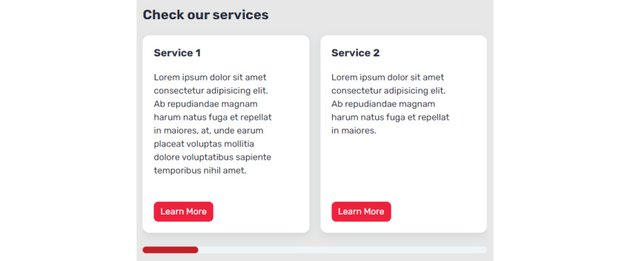
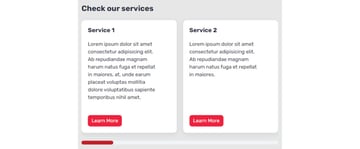
On medium screens, it would have this look:
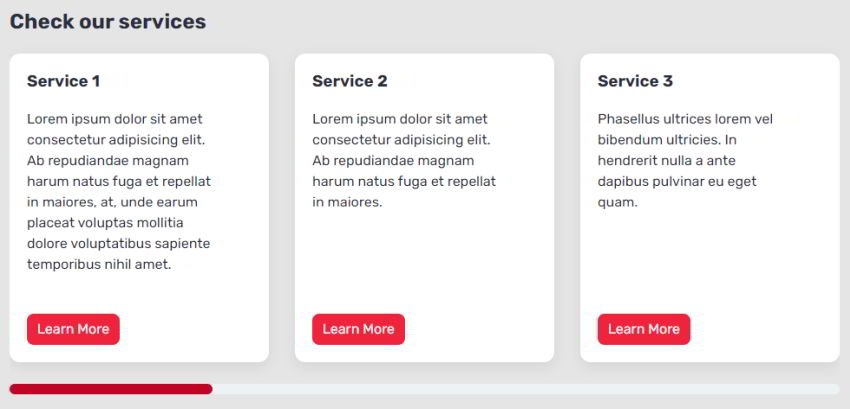
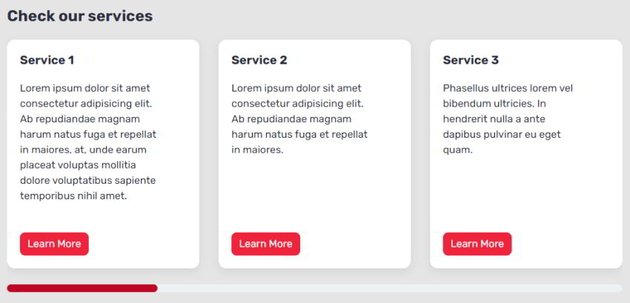
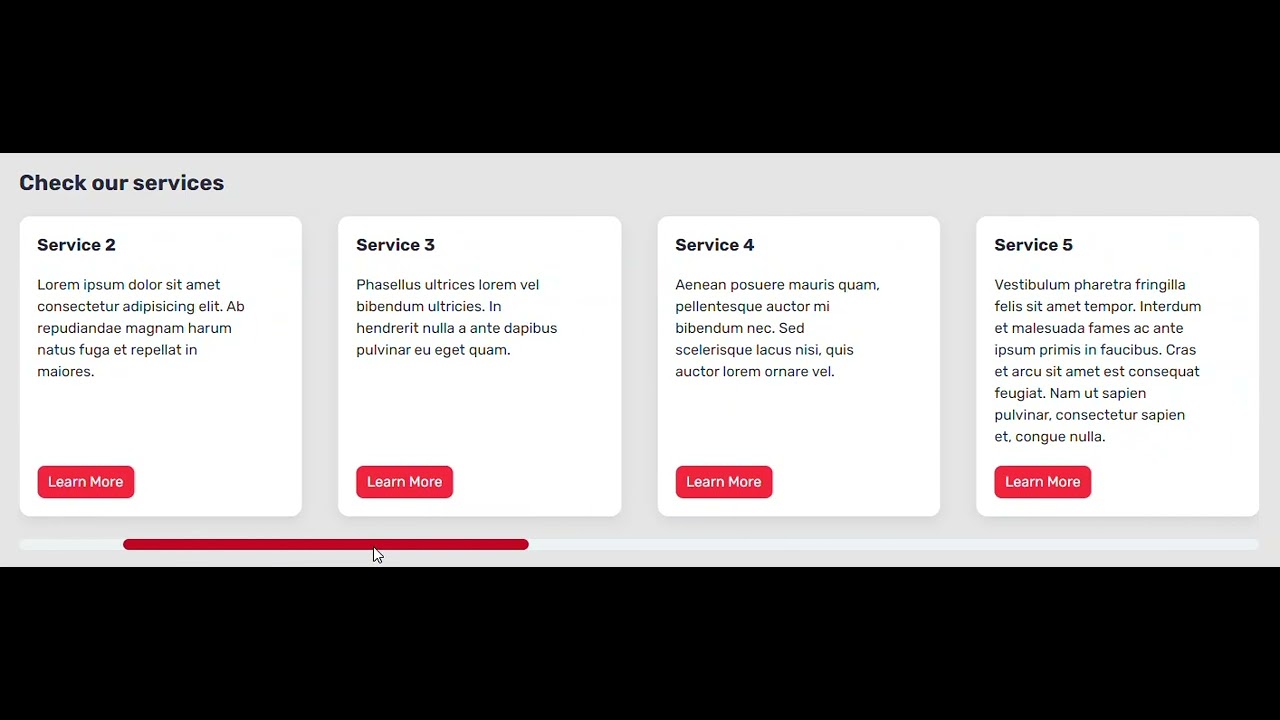
Lastly, on massive screens, it would look as follows:
We additionally have to lock (snap) the seen playing cards in place, every time a consumer has completed scrolling. This manner we’ll all the time have an actual variety of playing cards in view and we’ll keep away from seeing simply part of different playing cards; the scroll place will instantly shift to the place to begin of the closest card. This leap will produce an impact the place every set of seen playing cards will behave a bit like carousel slides.
This impact can be much more apparent on cellular screens the place solely a single card seems, and as you swipe, the adjoining card slides in.
To higher perceive what I’m describing, take into account the next video, and even higher, test the demos with varied display sizes:
2. Outline the HTML Markup
We’ll use a fairly simple construction for this: a container aspect with a heading and a listing of playing cards inside it. Every card will comprise a title, content material, and hyperlink. We’ll wrap these components round some additional divs to make sure that the hyperlink button will all the time sit on the backside of the cardboard.
This is the markup:
<div class="container">
<h2>...</h2>
<ul class="playing cards">
<li class="card">
<div>
<h3 class="card-title">...</h3>
<div class="card-content">...</div>
</div>
<div class="card-link-wrapper">
<a href="" class="card-link">...</a>
</div>
</li>
<!-- extra playing cards right here -->
</ul>
</div>
3. Specify the Primary Types
To construct the specified format and particularly the grid, we are able to use totally different format strategies. We’ll begin with a flexbox strategy after which proceed with a CSS Grid one.
For simplicity, we’ll solely focus on the essential CSS elements.
All playing cards will stay inside a container that may have a 1400px width.
Flexbox Card UI
The important thing issues concerning the card wrapper:
- It is going to be a flex container.
- It’s going to have
overflow-x: scroll, as we need to scroll horizontally to take a look at all playing cards. - We’ll want a customized scrollbar that may match our model colours, assuming our model’s major coloration is darkish pink.
The important thing issues about every card:
- It is going to be a flex container with
flex-directionset tocolumn. Which means that the flex objects can be stacked vertically alongside the primary axis. - As stated earlier, the hyperlink button ought to all the time be on the backside independently from the title and content material lengths of every card. So to realize this uniformity, we’ll give father or mother hyperlink wrapper
margin-top: auto. - We’ll give it
flex-shrink: 0as we don’t need to shrink and use theflex-basisproperty to set its width. Theflex-growproperty doesn’t curiosity us, so we’ll maintain the default0worth. The width will rely on the display dimension and margin between the adjoining playing cards. Let’s clarify.
On additional small screens, all playing cards could have a width equal to the father or mother width.
To calculate the cardboard width on small screens, we’ll do these calculations:
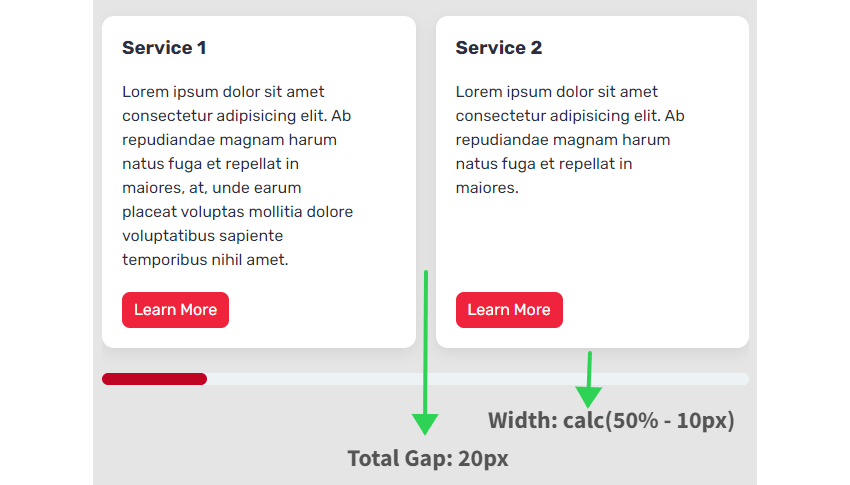
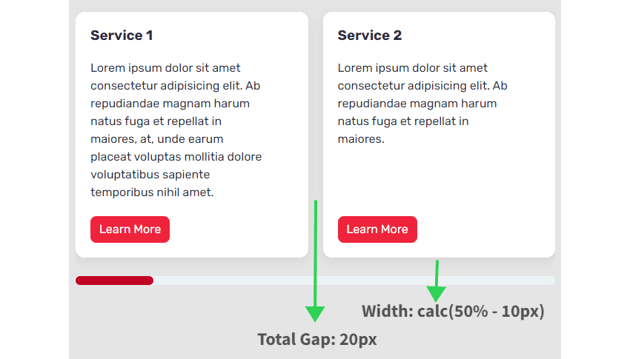

- Complete house between seen playing cards = 1 * 20px => 20px. We omit the house from the final card.
- The width of every card = calc(50% – 10px). The worth 10px derived by calculating: Complete house between seen playing cards / Variety of seen playing cards (20px / 2 => 10px).
To calculate the cardboard width on medium screens, we’ll do these calculations:
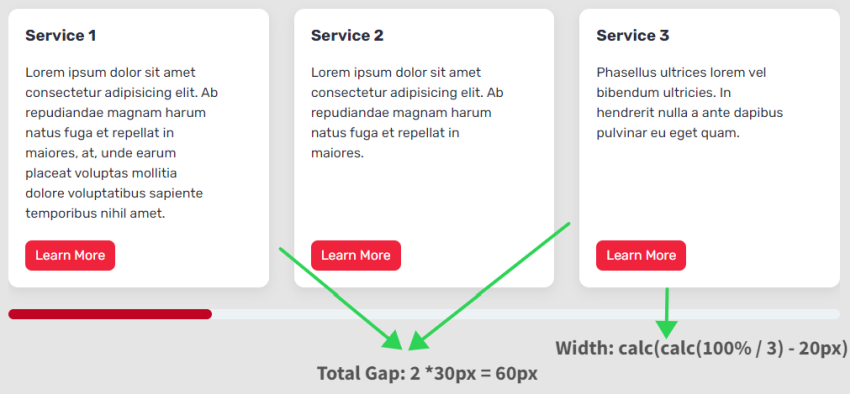

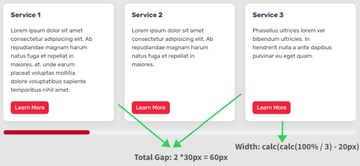
- Complete house between seen playing cards = 2 * 30px => 60px. We omit the house from the final card.
- The width of every card = calc(calc(100% / 3) – 20px). The worth 20px derived by calculating: Complete house between seen playing cards / Variety of seen playing cards (60px / 3 => 20px).
tip
We’d like a three-column format. So as a substitute of writing calc(33.333% – 20px), we’ll let browsers determine the precise share by including a nested calculation.
To calculate the cardboard width on massive screens, we’ll do these calculations:
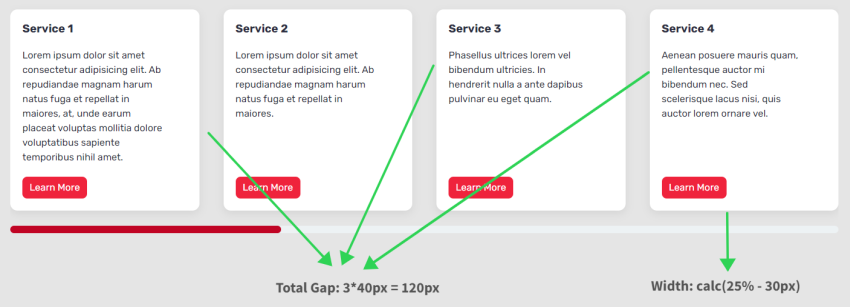


- Complete house between seen playing cards = 3 * 40px => 120px. We omit the house from the final card.
- The width of every card = calc(25% – 30px). The worth 30px derived by calculating: Complete house between seen playing cards / Variety of seen playing cards (120px / 4 => 30px).
To lock the viewport at sure components after scrolling has completed, we’ll use the CSS Scroll Snap characteristic. That stated:
- The cardboard wrapper will obtain the
scroll-snap-type: x obligatoryproperty worth. This ensures that the browser will snap to a snap level as quickly as consumer scrolling finishes. - Every card will obtain the
scroll-snap-align: beginproperty worth. This determines the a part of the cardboard at which the scrolling ought to cease. Attempt to give it one other worth likeheartto see the distinction.
Attempt additionally scrolling with out these two properties enabled to see the distinction.
Listed here are crucial types:
/*CUSTOM VARIABLES HERE*/
.playing cards {
show: flex;
overflow-x: scroll;
scroll-snap-type: x obligatory;
}
.card {
show: flex;
flex-direction: column;
flex: 0 0 100%;
scroll-snap-align: begin;
}
.card .card-link-wrapper {
margin-top: auto;
}
.playing cards::-webkit-scrollbar {
top: 12px;
}
.playing cards::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb,
.playing cards::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
border-radius: 92px;
}
.playing cards::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb {
background: var(--darkred);
}
.playing cards::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
background: var(--thumb);
}
@media (min-width: 500px) {
.card {
flex-basis: calc(50% - 10px);
}
.card:not(:last-child) {
margin-right: 20px;
}
}
@media (min-width: 700px) {
.card {
flex-basis: calc(calc(100% / 3) - 20px);
}
.card:not(:last-child) {
margin-right: 30px;
}
}
@media (min-width: 1100px) {
.card {
flex-basis: calc(25% - 30px);
}
.card:not(:last-child) {
margin-right: 40px;
}
}
And the associated CodePen demo the place you possibly can look at all of the types:
CSS Grid Card UI
On this second strategy we’ll create the identical card format, however with CSS Grid.
Listed here are the modifications we’ll apply:
- The cardboard wrapper can be a grid container.
- We’ll place all grid objects as columns due to the
grid-auto-flow: columnproperty worth. - We’ll use the
grid-auto-columnsproperty to set the dimensions for the columns. The column dimension will rely on the display dimension and the hole between every column. The calculations are precisely the identical as we did beforehand with theflex-basisproperty. So, the values of thegrid-auto-columnsproperty will match the values of the aforementionedflex-basisproperty at any display dimension.
data
We utilized the flex-basis property to the flex merchandise, then the grid-auto-columns property (and customarily all of the CSS Grid properties) to the grid container.
Listed here are the modified types:
/*CUSTOM VARIABLES HERE*/
.playing cards {
show: grid;
grid-auto-columns: 100%;
grid-column-gap: 10px;
grid-auto-flow: column;
}
@media (min-width: 500px) {
.playing cards {
grid-auto-columns: calc(50% - 10px);
grid-column-gap: 20px;
}
}
@media (min-width: 700px) {
.playing cards {
grid-auto-columns: calc(calc(100% / 3) - 20px);
grid-column-gap: 30px;
}
}
@media (min-width: 1100px) {
.playing cards {
grid-auto-columns: calc(25% - 30px);
grid-column-gap: 40px;
}
}
And once more, the associated CodePen demo the place you possibly can look at all of the types:
Conclusion
On this tutorial, we examined two methods of constructing a horizontal scrolling card UI. Alongside the best way, we went by way of varied fashionable CSS options. This can have given you some new information and has hopefully impressed you to create UI layouts that make the most of among the stuff we lined right here.
If you happen to can consider one other approach to construct this format, don’t neglect to share it with us! As all the time, thanks loads for studying!
Flexbox Tutorials on Tuts+
Flexbox is a notoriously difficult a part of CSS, however don’t fear, we’ve you lined!
[ad_2]